Anubis + Caddy
Caddy is a great reverse proxy tool that has been very useful in my lab. Nginx served me well for some time, but Caddy had me sold over its simplicity and the automatic HTTPS. Since then it has been a breeze making any changes or updates to my Caddy instance for anything I would want to do.
Anubis is an application that can run in-front or behind Caddy to protect your sites from bot traffic. For my use case I needed to protect multiple services behind one instance of Anubis. Even though Anubis is small and does not use much ram, I need to limit the number of duplicates running on my hosts. We can achieve a small setup by using two instances of Caddy, like directed in the Anubis docs. This way I do not need to run an instance of Anubis per service I would like to protect.
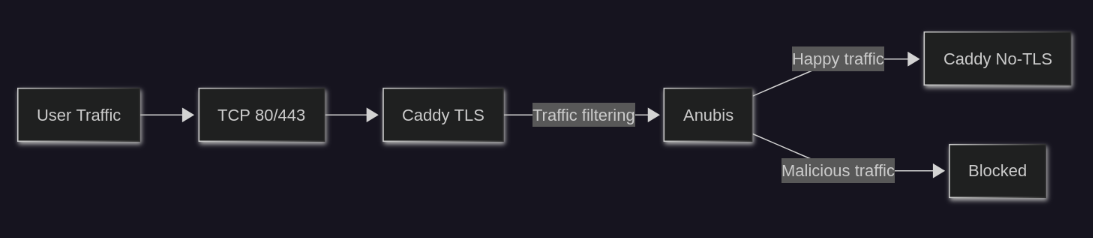
With this setup, all traffic for each of my domains route through Caddy and into Anubis instead of right to the back-end. Anubis will filter out the malicious traffic and send all the good traffic to the second Caddy, which will route the traffic finally to the correct service.
We can setup these both for our system using a docker-compose configuration. We are setting up one Caddy to listen on ports 80 and 443 and the other to listen on 7000. You can use any port for the second Caddy, we just need to route the traffic leaving Anubis somewhere to be handled and won't infinitely loop.
services:
caddy-notls:
image: caddy:2
command: caddy run --config /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
container_name: caddy-notls
restart: always
ports:
- 7000:7000
networks:
- default
volumes:
- /DATA/AppData/CaddyProx/Caddyfile:/etc/caddy/Caddyfile
- caddy_data:/data
- caddy_config:/config
caddy-tls:
image: caddy:2
container_name: caddy-tls
networks:
- default
command: caddy run --config /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
restart: always
ports:
- 80:80
- 443:443
volumes:
- /DATA/AppData/Caddy/Caddyfile:/etc/caddy/Caddyfile
- caddy_data:/data
- caddy_config:/config
anubis-all:
image: ghcr.io/techarohq/anubis:latest
container_name: anubis-prox
ports:
- 8081:8081
environment:
BIND: ":8081"
DIFFICULTY: "4"
METRICS_BIND: ":9091"
SERVE_ROBOTS_TXT: "true"
TARGET: "http://caddy-notls:7000"
POLICY_FNAME: "/data/cfg/botPolicy.yaml"
OG_PASSTHROUGH: "true"
OG_EXPIRY_TIME: "24h"
networks:
- default
volumes:
- "/DATA/AppData/anubis/botPolicy.yaml:/data/cfg/botPolicy.yaml:ro"
volumes:
caddy_data:
caddy_config:
Now we just need to configure the instances of Caddy. For the first Caddy (TLS) we can configure our sites like so.
# Caddyfile-TLS
example1.com {
reverse_proxy anubis-prox:8081
}
example2.com {
reverse_proxy anubis-prox:8081
}And for the No-TLS Caddy instance we can configure it the following way.
# Caddyfile-No-TLS
{
auto_https off
}
:7000 {
# First Site Example
@example1 {
header X-Forwarded-Host example1.com
}
handle @example1 {
reverse_proxy http://your-service-ip-here:port
handle /api/* {
reverse_proxy http://your-other-service-ip-here:port
}
}
# Second Site Example
@example2 {
header X-Forwarded-Host example2.com
}
handle @example2 {
reverse_proxy http://another-service-ip-here:port
}
handle {
respond "Not allowed! lol" 400
}
}
Now with these applications all setup, all of your traffic will route through Caddy --> Anubis --> and finally your service!
